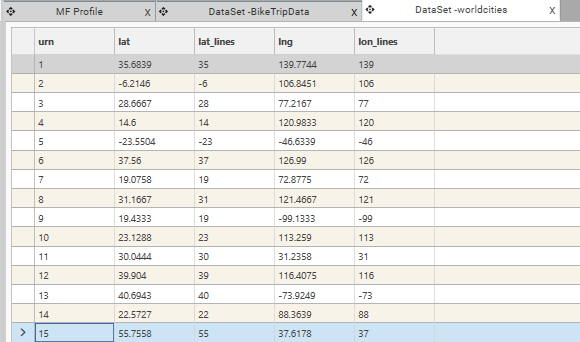
LMath: A
Creates an integer copy of Field A
Purpose
Use this function to:
- Turn a decimal field into a integer
- Create a copy of an existing numeric field
- Create a filtered copy of an existing field
- Create a copy of an existing field where null values are mapped to zero
Return Value
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| FieldType | Integer |
| FieldSize | Med - Up to 65,630 unique values High - up to 1,000,000 unique values Continuous - greater than 1,000,000 unique values |
| DataType | Discrete / Continuous |
| DataSize | Short / Integer |
Example Return Value: X...-X
e.g. 21, 98754654, -5, -654Parameters
| Parameter | JSON | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Table | “targetTable”: “MyTableName” | The target table on which the new field will be created |
| Filter | “dataset”: {DataSet_JSON} | Optional. If a filter is applied, records not in the filter recordset will be returned as null. Note: Records not in the filter will still be treated as null, even if [Treat Null as Zero] is true. |
| Math Function | “p1”: “A” | A |
| A | “p2”: “NumericFieldName” “p2”: “#N*.N*” | Required. Supports:
|
| Treat Null as Zero | "nullIsZero": true "nullIsZero": false | True/False. Default = False If true, then any null values in the input fields will be treated as if they have a value of 0. |
JSON Sample
{
"method": "BuildBakedField",
"project": "JoinDiscreteContinuous",
"targetTable": "worldcities",
"overwrite": true,
"name": "lat_lines",
"function": "lmath",
"p1": "A",
"p2": "lat"
}Usage Notes
Note: no rounding of data occurs when using A(LMath) to convert a decimal to an integer. The integer portion of the decimal number is kept, and the decimal portion is discarded.
See Also:
- LMath Overview
- A(DMath)
- CopyDiscrete
Example
| Example | Details |
|---|---|
| Description | Obtain integer portion of longitude |
| Input |
|
| Sample | 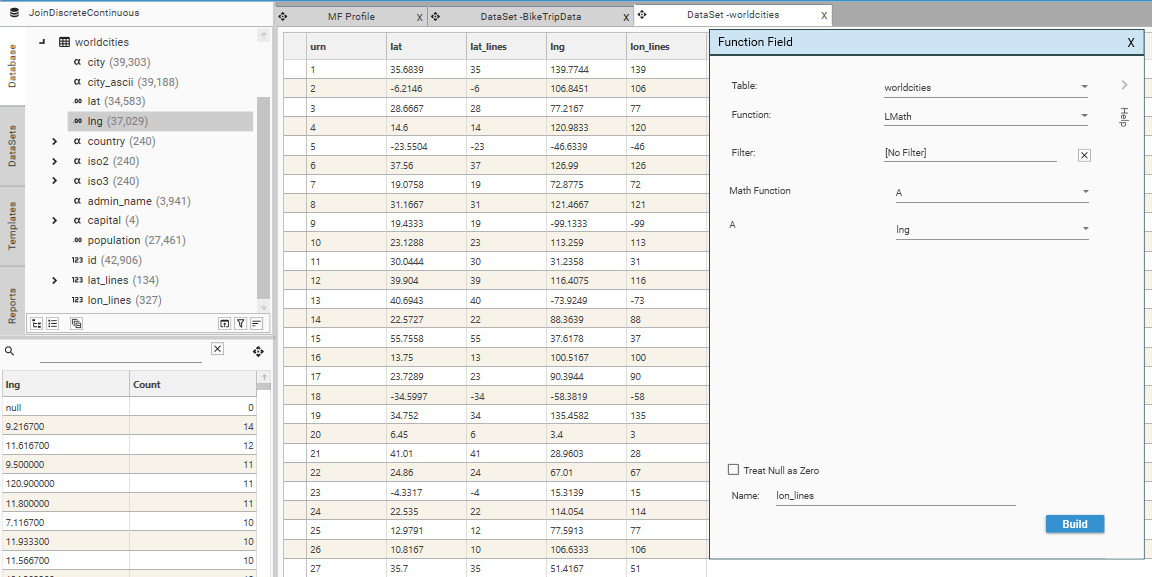 |