LMath Functions
LMath functions produce INTEGER fields from inputs ranging from A-E (depending on the function)
Purpose
Use LMATH functions to:
- Convert a double to an integer
- Manipulate integer data
Return Value
| Property | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| FieldType | Integer | LMATH functions always return an Integer |
| FieldSize | Low, Med. High | Med - Up to 65,630 unique values High - up to 1,000,000 unique values Continuous - greater than 1,000,000 unique values |
| DataType | Discrete/ Continuous | Depends on inputs and calculation |
| DataSize | Short / Integer |
Example Return Value: X...-X
e.g. 21, 98754654, -5, -654Data View
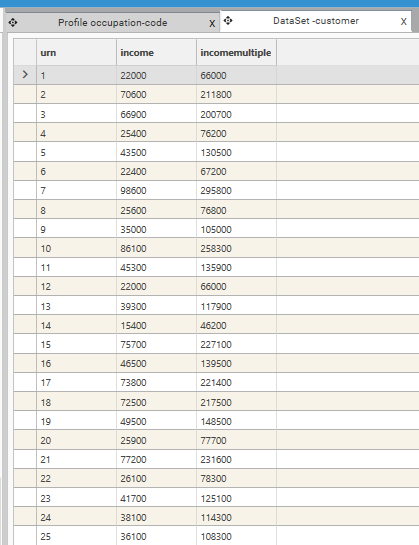
Quick Profiler and Tree view
Parameters
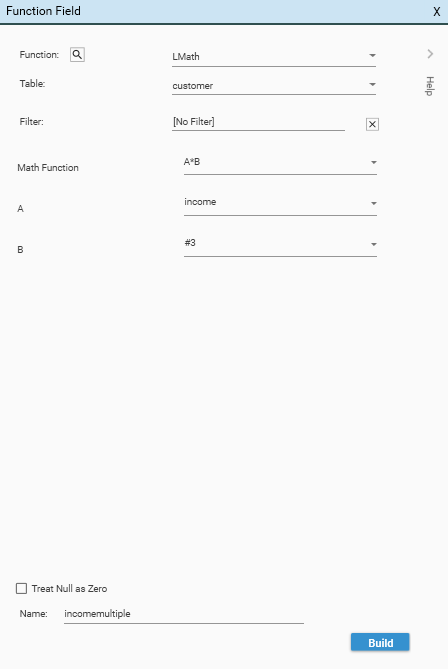
| Parameter | JSON | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Table | “targetTable”: “MyTableName” | The target table on which the new field will be created |
| Filter | “dataset”: {DataSet_JSON} | Optional. If a filter is applied, records not in the filter recordset will be returned as null. |
| Function | "function":"lmath" | |
| MATH Function | “p1”: “” | Select the LMATH function from the drop-down list. Specifies the function to use. |
| A -E | “p2-7”: “FieldName” “p2-7”: “#N*” | Fields to use for the values A-D. Alternatively, a field can be replaced with a Fixed Value. Fixed values must be preceded by the hash symbol (#). Supports:
|
| Name | "name" : "FieldName" | Required. The name of the field to create. |
JSON Sample

Usage Notes
See Also: