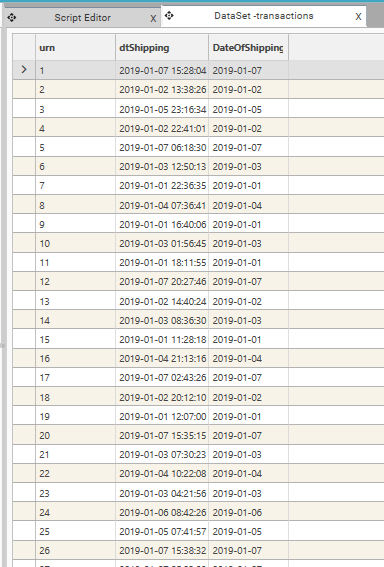
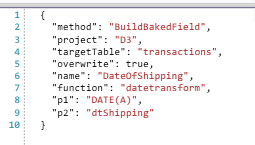
Date Transform: DATE(A)
Turns a continuous DateTime field into a discrete Date field, or creates a copy of a Date field.
Purpose
Use this function to:
- Create a copy of an existing date field
- Create a discrete Date field from a continuous DateTime field
- Create a single fixed date field
Return Value
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| FieldType | Date |
| FieldSize | Med |
| DataType | Discrete |
| DataSize | Short |
Example Return Value: 2021-01-05
Parameters
| Parameter | JSON | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Table | “targetTable”: “MyTableName” | The target table on which the new field will be created |
| Filter | “dataset”: {DataSet_JSON} | Optional. If a filter is applied, records not in the filter Recordset will be returned as null. |
| DateTimeFunction | “p1”: “DATE(A)” | DATE(A) |
| A | “p2”: “DateTimeFieldName” “p2”: “DateFieldName” “p2”: “#YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS” “p2”: “#YYYY-MM-DD” | Required. Supports:
|
JSON Sample
Usage Notes
To create copies of date fields with a subset of all available values, use DATE(A) with a filter.
Use DATE(A) to create a discrete Date field from a continuous DateTime field so that the field can be used in analytics and engineering that do not support continuous fields.
Example
| Example | Details |
|---|---|
| Description | Create a date field from DateTime field |
| Input |
|
| Sample | 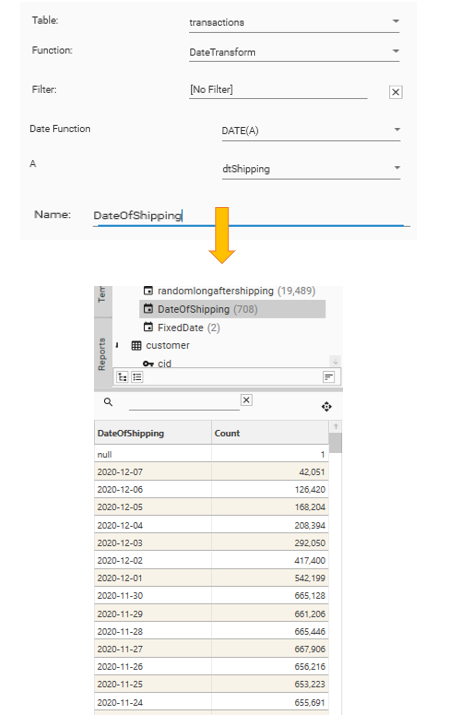 |